Managing foot ulcers is a critical concern for those affected, especially individuals with diabetes or vascular disease. Foot ulcers can lead to severe complications if not properly managed. Understanding the causes, implementing effective prevention strategies, and knowing the best care practices are essential steps in managing foot ulcers successfully. This comprehensive guide delves into these aspects to help you navigate the challenges of foot ulcers and maintain foot health.
Introduction
Foot ulcers are a significant health issue, often resulting from underlying medical conditions such as diabetes and peripheral artery disease. These open sores or wounds on the feet can become infected if not treated promptly, leading to serious complications. Managing foot ulcers involves a multifaceted approach that includes understanding their causes, implementing preventive measures, and applying effective care techniques. In this guide, we explore these aspects in detail to provide a holistic approach to managing foot ulcers.
Understanding Foot Ulcers
Foot ulcers are open sores that develop on the skin, typically on the soles of the feet. They occur when the skin breaks down, exposing the underlying tissues. Foot ulcers can vary in severity from superficial to deep wounds that reach the bone. They are particularly common in individuals with diabetes, where they are often a result of neuropathy (nerve damage) and peripheral artery disease.
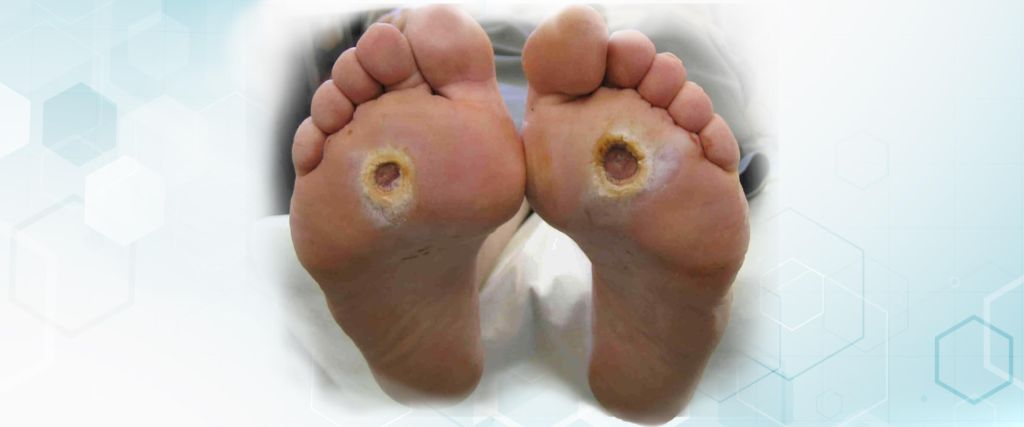
Causes of Foot Ulcers
Diabetes: Diabetes is a leading cause of foot ulcers. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves (diabetic neuropathy), reducing sensation in the feet. This makes it easier for injuries to go unnoticed and become ulcers. Additionally, diabetes can cause poor circulation, impeding the healing process.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): PAD reduces blood flow to the extremities, making it difficult for wounds to heal. Reduced blood flow can also lead to tissue death, increasing the risk of ulcers.
Neuropathy: Nerve damage, often due to diabetes, can lead to a loss of sensation in the feet. Without feeling pain, minor injuries or pressure points can go unnoticed and develop into ulcers.
Foot Deformities: Conditions such as hammertoes, bunions, or Charcot foot can cause abnormal pressure points on the feet, leading to ulcers.
Inadequate Footwear: Poorly fitting shoes can cause friction and pressure points, leading to blisters and ulcers.
Infections: Bacterial infections can quickly exacerbate foot ulcers, especially in individuals with compromised immune systems.
Prevention of Foot Ulcers
Regular Foot Inspections: Daily inspection of the feet is crucial for early detection of potential problems. Look for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or any changes in the skin.
Proper Foot Hygiene: Keep the feet clean and dry. Wash them daily with mild soap and lukewarm water, and dry thoroughly, especially between the toes.
Moisturize: Use moisturizers to prevent dry, cracked skin, but avoid applying lotion between the toes to prevent fungal infections.
Proper Footwear: Wear shoes that fit well and provide adequate support. Avoid high heels and tight shoes that can cause pressure points.
Use Protective Footwear: Always wear shoes, even indoors, to protect your feet from injuries.
Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider for foot exams can help detect problems early.
Blood Sugar Control: For diabetics, maintaining good blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing complications, including foot ulcers.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking impairs circulation, which can hinder healing and increase the risk of foot ulcers.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the feet, increasing the risk of ulcers.
Managing Foot Ulcers
Initial Assessment: When a foot ulcer is identified, a thorough assessment by a healthcare professional is necessary. This includes determining the size, depth, and severity of the ulcer, as well as checking for signs of infection.
Cleaning the Ulcer: Proper cleaning of the ulcer is crucial. Use a saline solution or mild soap and water to clean the wound. Avoid using hydrogen peroxide or iodine, as these can damage tissue.
Debridement: Removing dead or infected tissue from the ulcer (debridement) promotes healing. This should be done by a healthcare professional.
Dressing the Ulcer: Use appropriate dressings to keep the ulcer moist and protected. Options include hydrocolloid, foam, or alginate dressings, depending on the ulcer’s characteristics.
Offloading: Reducing pressure on the ulcerated area is essential. This can be achieved through the use of specialized footwear, orthotics, or even bed rest in severe cases.
Infection Control: If an infection is present, antibiotics may be necessary. Topical or oral antibiotics can help control the infection and promote healing.
Monitoring and Follow-up: Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is important to monitor the ulcer’s progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Advanced Treatments: In some cases, advanced treatments such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy, skin grafts, or growth factor treatments may be considered.
Living with Foot Ulcers
Living with foot ulcers requires ongoing care and attention to prevent complications and promote healing. Here are some strategies for managing daily life with foot ulcers:
Adherence to Treatment Plans: Follow the treatment plan prescribed by your healthcare provider diligently. This includes taking medications, attending follow-up appointments, and adhering to wound care protocols.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Making lifestyle adjustments can help manage foot ulcers more effectively. This includes dietary changes to manage blood sugar levels, regular exercise to improve circulation, and avoiding activities that put excessive pressure on the feet.
Emotional Support: Managing a chronic condition like foot ulcers can be emotionally challenging. Seek support from family, friends, or support groups to help cope with the stress and anxiety that may accompany this condition.
Education: Educate yourself about foot ulcers and their management. Understanding the condition and its treatment options can empower you to take control of your health.
Foot Ulcers and Diabetes
Diabetes is a major risk factor for foot ulcers. The combination of neuropathy and poor circulation in diabetics creates a perfect storm for the development of ulcers. Managing foot ulcers in diabetic patients requires a comprehensive approach:
Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining blood sugar levels within the target range is crucial. This helps prevent further nerve damage and improves healing.
Regular Foot Exams: Diabetic patients should have their feet examined regularly by a healthcare professional. Early detection of problems can prevent ulcers from developing or worsening.
Foot Care Education: Diabetic patients should be educated on proper foot care techniques, including daily inspections, proper hygiene, and the importance of wearing appropriate footwear.
Multi-disciplinary Approach: Managing foot ulcers in diabetics often requires a team approach, involving primary care physicians, endocrinologists, podiatrists, and wound care specialists.
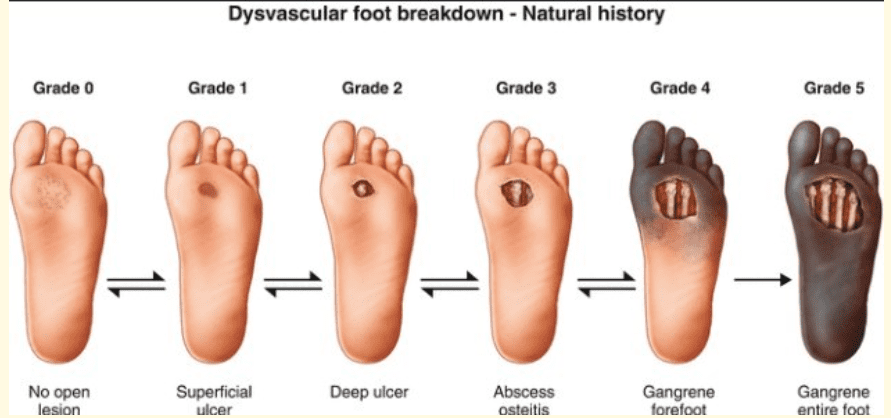
Foot Ulcers in the Elderly
Elderly individuals are also at an increased risk for foot ulcers due to factors such as reduced mobility, poor circulation, and the presence of other chronic conditions. Specific considerations for managing foot ulcers in the elderly include:
Mobility Aids: Use of mobility aids such as walkers or canes can help reduce pressure on the feet and prevent ulcers.
Home Safety: Ensure the home environment is safe and free of hazards that could cause foot injuries.
Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition is important for wound healing. Ensure the elderly have a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
Caregiver Support: Caregivers play a crucial role in helping the elderly manage foot ulcers. They can assist with daily foot inspections, wound care, and ensuring adherence to treatment plans.
Common Myths about Foot Ulcers
Myth: Foot Ulcers Are Not Serious: Foot ulcers are a serious health issue and can lead to severe complications if not treated properly. They should never be ignored.
Myth: Only Diabetics Get Foot Ulcers: While diabetics are at a higher risk, anyone can develop foot ulcers, especially those with poor circulation or neuropathy.
Myth: Foot Ulcers Will Heal on Their Own: Foot ulcers require proper treatment and care to heal. Without intervention, they can worsen and become infected.
Myth: Amputation Is Inevitable: While severe cases of foot ulcers may lead to amputation, many ulcers can be treated and managed with appropriate care.
Nutritional Considerations for Foot Ulcer Management
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in wound healing. Certain nutrients are particularly important for individuals managing foot ulcers:
Protein: Protein is essential for tissue repair and wound healing. Ensure an adequate intake of high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, eggs, dairy, and legumes.
Vitamin C: Vitamin C is crucial for collagen formation and immune function. Include fruits and vegetables rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers.
Zinc: Zinc supports immune function and wound healing. Good sources of zinc include meat, shellfish, dairy products, and nuts.
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is important for overall health and wound healing. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Avoiding High Sugar Foods: For diabetics, controlling blood sugar levels is essential. Avoid foods high in sugar and refined carbohydrates.
Physical Activity and Foot Ulcers
Physical activity is important for overall health and can aid in the management of foot ulcers by improving circulation and blood sugar control. However, it’s important to choose activities that do
not put excessive pressure on the feet:
Low-Impact Exercises: Activities such as swimming, cycling, and yoga are gentle on the feet and can improve circulation.
Foot Care During Exercise: Wear appropriate footwear during exercise to protect the feet and prevent injuries.
Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain in the feet during exercise. If any issues arise, stop the activity and check for potential problems.
Innovations in Foot Ulcer Treatment
Advancements in medical technology have led to new and innovative treatments for foot ulcers:
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): HBOT involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which can promote wound healing by increasing oxygen delivery to the tissues.
Growth Factor Therapy: Growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell growth and healing. They can be applied topically to foot ulcers to promote healing.
Skin Substitutes: Bioengineered skin substitutes can be used to cover and protect foot ulcers, promoting healing.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): NPWT involves applying a vacuum to the wound, which can help remove excess fluid and promote healing.
Role of Podiatrists in Managing Foot Ulcers
Podiatrists are healthcare professionals who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of foot and ankle conditions, including foot ulcers. Their role in managing foot ulcers includes:
Assessment and Diagnosis: Podiatrists can assess the severity of foot ulcers and determine the best course of treatment.
Debridement: Podiatrists are skilled in performing debridement to remove dead or infected tissue from ulcers.
Offloading Techniques: Podiatrists can recommend and provide specialized footwear and orthotics to reduce pressure on foot ulcers.
Patient Education: Podiatrists educate patients on proper foot care techniques to prevent and manage foot ulcers.
Psychological Impact of Foot Ulcers
Living with foot ulcers can have a significant psychological impact, including feelings of anxiety, depression, and frustration. Addressing the emotional aspects of foot ulcers is an important part of comprehensive care:
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who are experiencing similar challenges.
Counseling: Professional counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional stress of managing foot ulcers.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce stress and improve emotional well-being.
FAQs
What causes foot ulcers?
Foot ulcers can be caused by several factors, including diabetes, peripheral artery disease, neuropathy, foot deformities, inadequate footwear, and infections.
How can I prevent foot ulcers?
Prevent foot ulcers by maintaining good foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, inspecting your feet daily, controlling blood sugar levels, and avoiding smoking.
What should I do if I develop a foot ulcer?
Seek prompt medical attention. Clean the ulcer, keep it dressed, and follow your healthcare provider’s treatment plan. Avoid putting pressure on the ulcer.
Are foot ulcers common in diabetics?
Yes, foot ulcers are common in diabetics due to neuropathy and poor circulation. Proper foot care and regular medical check-ups are crucial for prevention.
Can foot ulcers be treated at home?
While initial care can be managed at home, it is important to seek medical advice for proper assessment and treatment. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions closely.
What are the signs of an infected foot ulcer?
Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, pus, foul odor, and increased pain. If you suspect an infection, seek medical attention immediately.
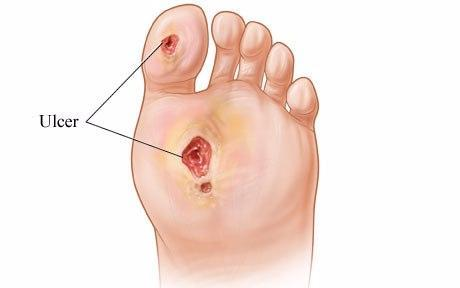
Conclusion
Managing foot ulcers involves a comprehensive approach that includes understanding their causes, implementing preventive measures, and applying effective care techniques. By adhering to proper foot care routines, seeking prompt medical attention for any foot problems, and making lifestyle adjustments, individuals can successfully manage foot ulcers and maintain foot health. Whether you are at risk of developing foot ulcers or currently managing them, this guide provides the essential knowledge and strategies to navigate the challenges and promote healing.
Our Doctors
Dedicated IR Center for Vascular Problems in Madhya Pradesh
DR. SHAILESH GUPTA
MD, PDCC (INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY) Consultant & Co-Director CVIC (Center Of Vascular & Interventional Care)
DR. ALOK KUMAR UDIYA
MD Radiology, PDCC (Neurointervention Radiology), PDCC ( HPB Intervention Radiology) FINR (Switzerland) & EBIR
Endovascular Surgeon & Consultant Interventional Neuroradiologist at Care CHL Hospital, Indore Co-director CVIC( center for vascular and interventional care)
DR. NISHANT BHARGAVA
Consultant Intervention Radiologist
MD Radiology, PDCC ( Neurointervention Radiology), FINR ( Fellowship in Neurointervention Radiology)
Co-director CVIC(Center for Vascular and Interventional Care)
Contact Details
Phone no.
0731 4675670
+91 9827760073
Facebook
https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100092538633553&mibextid=ZbWKwL
Instagram
https://instagram.com/cvic_center?igshid=ZGUzMzM3NWJiOQ==
Google My business
https://g.co/kgs/DrdV3T
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCP5TH5e4iQZkpDUgnLsgZhw
Pinterest
https://pin.it/5DzpX5Z
Twitter
https://x.com/cviccenter?t=01TclSrLFdu0K2re0Gs96w&s=08
LINKEDIN
https://www.linkedin.com/company/center-of-vascular-interventional-care/
Location –
Read More –
Uterine Artery Embolization: A Revolutionary Approach to Fibroid Treatment – https://cvicvascular.com/uterine-artery-embolization-a-revolutionary-approach-to-fibroid-treatment/
What Happens to the Baby During Placenta Previa? – https://cvicvascular.com/what-happens-to-the-baby-during-placenta-previa/
Is Peripheral Angioplasty Painful? What to Expect and How Pain is Managed – https://cvicvascular.com/is-peripheral-angioplasty-painful/