Understanding the Differences Between TIPS and BRTO Procedures in Gastroenterology
In the field of gastroenterology, particularly in the management of complications from liver disease, two significant procedures stand out: Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) and Balloon-Occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration (BRTO). Both treatments are designed to manage portal hypertension—a common consequence of advanced liver disease—but they do so in different ways and for different indications. This blog will explore the distinctions between TIPS and BRTO, their applications, benefits, and risks, to provide a comprehensive understanding of these two critical procedures.
What is TIPS?
TIPS is a minimally invasive procedure that creates a pathway within the liver to connect the portal vein (which carries blood from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver) to one of the hepatic veins (which carry blood away from the liver back to the heart). This connection is made using a shunt—a small tube that is placed between the two vessels to redirect blood flow, thus reducing the high pressure in the portal vein.
Applications of TIPS:
- Treatment of variceal bleeding that doesn’t respond to medical therapy or endoscopic treatments.
- Management of refractory ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdomen due to high portal pressure).
- Other complications of portal hypertension, such as hepatic hydrothorax (fluid accumulation in the chest).
Benefits of TIPS:
- Provides a significant decrease in portal pressure.
- Reduces the risk of recurrent bleeding and accumulation of fluid.
- Serves as a bridge to liver transplantation for some patients.
Risks of TIPS:
- Potential for worsening liver function.
- Risk of encephalopathy, a brain disorder caused by the liver’s inability to remove toxins from the blood.
- Shunt dysfunction or occlusion.
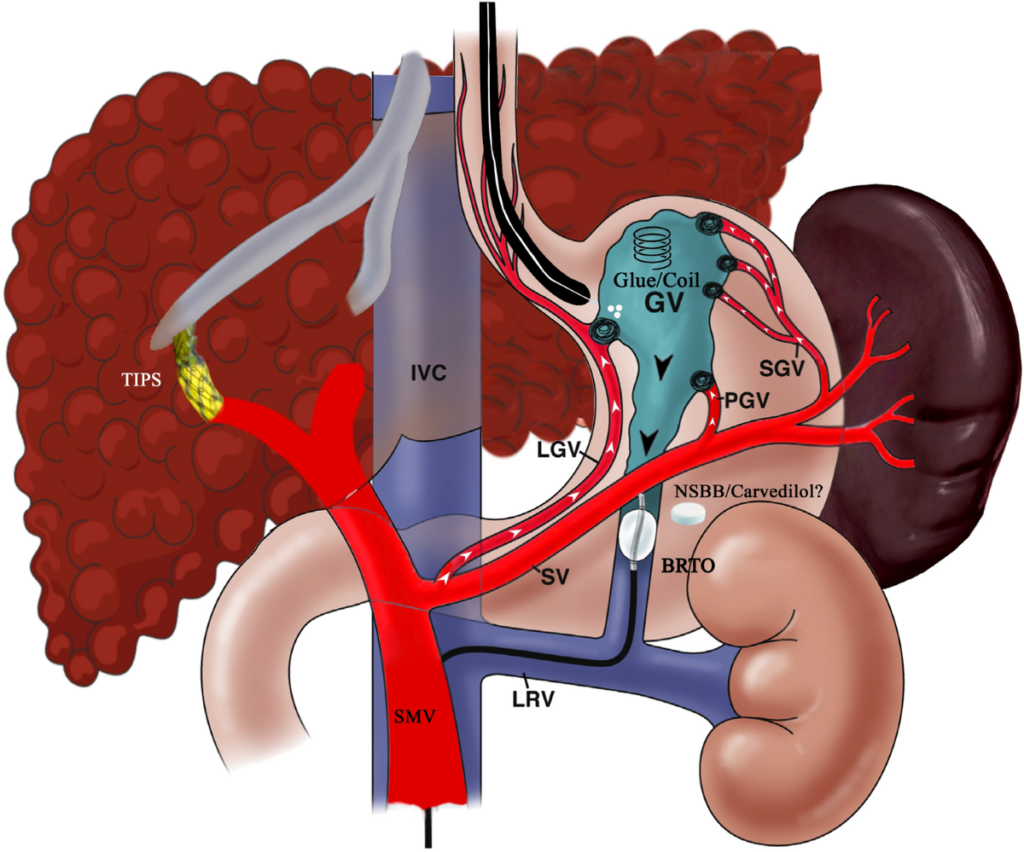
What is BRTO?
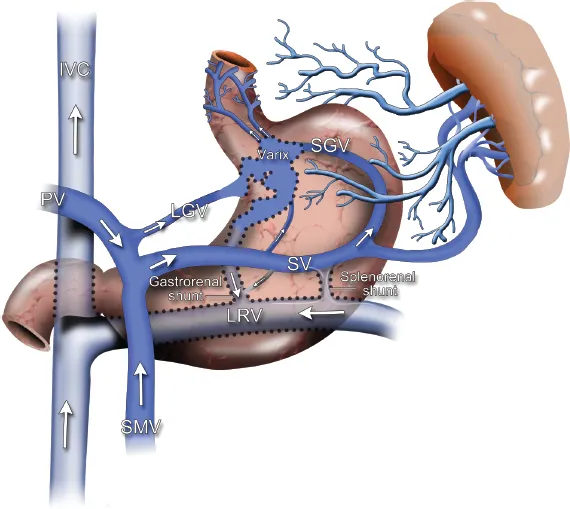
BRTO, on the other hand, is a procedure that involves the occlusion of varices (abnormally dilated veins) in the gastric system using a balloon catheter and sclerosant (a substance that scars the veins, causing them to close). The BRTO procedure is specifically used to manage gastric varices, which can be a source of significant bleeding in patients with portal hypertension.
Applications of BRTO:
Balloon-Occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration (BRTO) is a specialized interventional radiology procedure used primarily in the treatment of gastric varices, which are dilated veins in the stomach that can bleed heavily. Here are the primary applications of BRTO in gastroenterology:
Treatment of Gastric Varices:
- Bleeding Prevention: BRTO is highly effective for preventing bleeding in patients with gastric varices, especially those at high risk of rupture. It is often used when endoscopic treatments are not feasible or have failed.
- Acute Bleeding: In cases of active bleeding, BRTO can be an emergency treatment option to stabilize the patient by occluding the bleeding varices.
Management of Hepatorenal Syndrome: BRTO can indirectly help improve renal function in patients with hepatorenal syndrome by improving hemodynamics and reducing the release of vasoactive substances that worsen kidney function.
Improving Liver Function: By reducing the shunting of blood away from the liver, BRTO can help in improving portal venous flow, which may enhance liver function, particularly in cases where a large volume of blood is shunted away from the liver.
Complementary Therapy to TIPS: In some cases, BRTO is used alongside TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) when TIPS alone is insufficient to manage the complications related to portal hypertension, or when TIPS increases the risk or severity of gastric varices.
Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy: Although not its primary indication, BRTO can sometimes help in reducing episodes of hepatic encephalopathy by improving the overall liver blood flow and reducing the toxins that reach the brain due to bypassing the liver in portal circulation.
BRTO is particularly beneficial for patients who are not candidates for other forms of intervention like TIPS due to their specific condition or complications. It provides a targeted approach to manage potentially life-threatening varices with a relatively low impact on the rest of the body’s systems.
Benefits of BRTO:
- High efficacy in controlling and preventing rebleeding from gastric varices.
- Improves liver function in some cases by redirecting blood flow through the liver, enhancing its ability to filter toxins.
- Less impact on systemic circulation compared to TIPS.
Risks of BRTO:
- Potential for complications from the sclerosant, including pain and fever.
- Risk of worsening ascites or the development of new varices as portal pressure may increase in other areas.
Key Differences Between TIPS and BRTO
- Purpose and Focus: TIPS is used to lower overall portal pressure and treat various complications of portal hypertension, whereas BRTO is specifically aimed at treating gastric varices.
- Procedure Technique: TIPS involves creating a shunt within the liver to bypass the liver, while BRTO involves blocking off blood flow to specific varices using a balloon and sclerosant.
- Impact on Liver Function: TIPS can potentially worsen liver function due to the diversion of blood flow, whereas BRTO may actually improve liver function by redirecting some blood back through the liver tissue.
- Indications: TIPS is generally indicated for more diffuse complications of portal hypertension, like variceal bleeding and refractory ascites, across the GI tract. BRTO is more narrowly focused on preventing bleeding from gastric varices.
Here’s a table summarizing the differences between TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) and BRTO (Balloon-Occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration) procedures in gastroenterology:
| Feature | TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) | BRTO (Balloon-Occluded Retrograde Transvenous Obliteration) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces overall portal pressure; treats various complications of portal hypertension. | Specifically targets and treats bleeding from gastric varices. |
| Technique | Creates a shunt within the liver to connect portal and hepatic veins to bypass the liver. | Uses a balloon catheter and sclerosant to occlude varices in the gastric system. |
| Indications | Variceal bleeding, refractory ascites, hepatic hydrothorax. | Gastric varices at risk of bleeding, particularly when TIPS is unsuitable. |
| Impact on Liver Function | Can worsen liver function due to diversion of blood flow from the liver. | May improve liver function by redirecting some blood flow through the liver tissue. |
| Impact on Systemic Circulation | Lesser impact as it diverts blood away from the liver. | Significant impact as it enhances the liver’s filtration capacity by increasing flow through liver tissues. |
| Risks | Risk of encephalopathy, shunt dysfunction, worsening liver function. | Complications from sclerosant (pain, fever), potential for worsening ascites or developing new varices. |
| Benefits | Decreases portal pressure, reduces risk of bleeding and fluid accumulation, bridge to liver transplantation. | Effective in controlling and preventing rebleeding from gastric varices, less systemic impact than TIPS. |
This table offers a clear comparison of these two important gastroenterological procedures. It presents them side-by-side. It highlights their unique purposes, techniques, and indications. Also outlines their impacts, risks, and benefits.
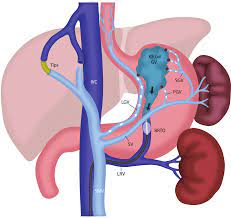
Conclusion
Both TIPS and BRTO are vital procedures in the management of portal hypertension. They have specific roles based on the patient’s condition and the nature of their portal hypertension. Deciding between these two procedures depends on multiple factors. These factors include the specific indications. They also include the patient’s overall liver function. Additionally, the presence of complications such as ascites or variceal bleeding is considered. Like any medical treatment, consultations with a specialist in hepatology and gastroenterology are essential. This helps to choose the appropriate intervention based on a comprehensive evaluation of the patient.
Our Doctors
Dedicated IR Center for Vascular Problems in Madhya Pradesh
DR. SHAILESH GUPTA
MD, PDCC (INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY) Consultant & Co-Director CVIC (Center Of Vascular & Interventional Care)
DR. ALOK KUMAR UDIYA
MD Radiology, PDCC (Neurointervention Radiology), PDCC ( HPB Intervention Radiology) FINR (Switzerland) & EBIR
Endovascular Surgeon & Consultant Interventional Neuroradiologist at Care CHL Hospital, Indore Co-director CVIC( center for vascular and interventional care)https://interventionradiologyindore.com/
DR. NISHANT BHARGAVA
Consultant Intervention Radiologist
MD Radiology, PDCC ( Neurointervention Radiology), FINR ( Fellowship in Neurointervention Radiology)
Co-director CVIC(Center for Vascular and Interventional Care)
Contact Details
Phone no.
0731 4675670
+91 9827760073
Facebook
https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100092538633553&mibextid=ZbWKwL
Instagram
https://instagram.com/cvic_center?igshid=ZGUzMzM3NWJiOQ==
Google My business
https://g.co/kgs/DrdV3T
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCP5TH5e4iQZkpDUgnLsgZhw
Pinterest
https://pin.it/5DzpX5Z
Twitter
https://x.com/cviccenter?t=01TclSrLFdu0K2re0Gs96w&s=08
LINKEDIN
https://www.linkedin.com/company/center-of-vascular-interventional-care/
Location
Differences Between TIPS and BRTO Procedures in Gastroenterology
Read More –
Revolutionizing Blood Flow: The Ultimate Guide to Peripheral Angioplasty – https://cvicvascular.com/peripheral-angioplasty/
Varicose Vein Treatment: Endovenous Laser Therapy – https://cvicvascular.com/varicose-vein-treatment-endovenous-laser-therapy/
Thrombolysis: Definition, Types, Uses, Effects, and More – https://cvicvascular.com/thrombolysis/