What Causes Gangrene? A Comprehensive Guide
Gangrene is a serious medical condition that occurs when a lack of blood flow or infection causes tissue in the body to die. It typically affects the extremities, such as the toes, fingers, or limbs, but it can also develop internally. Understanding the causes, types, and risk factors of gangrene is crucial for early detection and treatment. This blog delves into what gangrene is, what causes it, and how to prevent it.
What Is Gangrene?
Gangrene happens when the body’s tissues die due to insufficient blood supply or infection. Blood flow carries essential nutrients and oxygen to tissues; when this flow is interrupted, the tissues starve, leading to cell death. Gangrene can spread rapidly, and without immediate medical intervention, it can become life-threatening.
Types of Gangrene
- Dry Gangrene: This type occurs when there is a blockage in the blood vessels, often caused by conditions like diabetes, arteriosclerosis, or frostbite. The skin becomes dry, shriveled, and dark in color. Dry gangrene develops slowly and isn’t typically associated with infections.
- Wet Gangrene: Caused by bacterial infections, wet gangrene occurs when tissue becomes moist and swells due to a lack of blood supply and infection. It is commonly associated with injuries, burns, or surgical wounds. This type progresses rapidly and can be life-threatening if untreated.
- Gas Gangrene: This rare but serious type is caused by a bacterial infection known as Clostridium perfringens, which releases gas into tissues. It is characterized by severe pain, swelling, and the production of gas bubbles under the skin. Gas gangrene is a medical emergency.
- Internal Gangrene: This type occurs inside the body, often affecting organs like the intestines, gallbladder, or appendix due to lack of blood flow or infection. It is harder to detect than external gangrene and can cause sepsis, a life-threatening infection of the bloodstream.
- Fournier’s Gangrene: This rare type of gangrene affects the genital area and is caused by a bacterial infection. It typically occurs in men and is a medical emergency.
Also Read: How Can I Prevent Diabetic Foot Problems? 10 Essential Tips for Healthy Feet
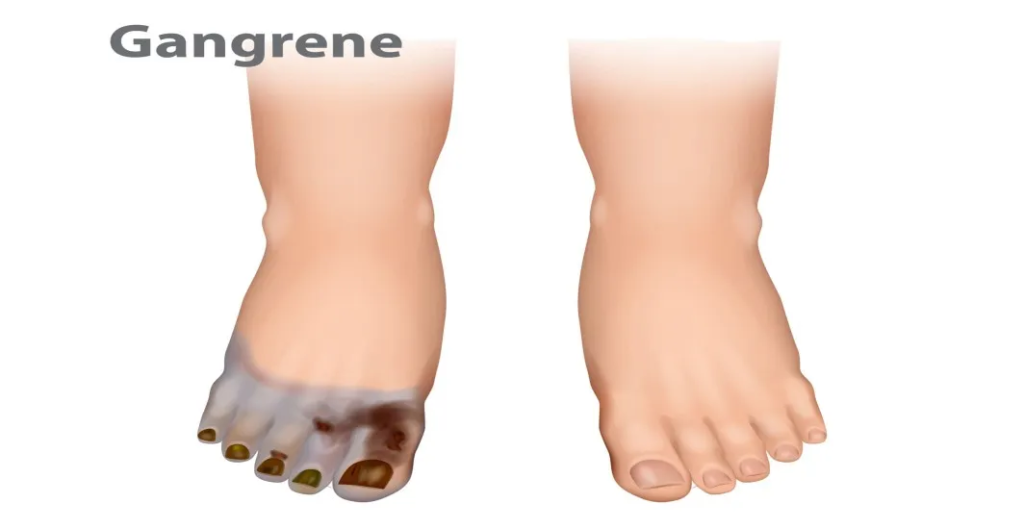
Causes of Gangrene
Several factors can cause gangrene. The most common include:
1. Lack of Blood Flow
Blood circulation issues, such as atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), can prevent oxygen and nutrients from reaching tissues. Conditions like diabetes, which can damage blood vessels over time, significantly increase the risk of gangrene.
2. Infections
Severe bacterial infections, particularly those that go untreated, can lead to gangrene. Wet and gas gangrene are often caused by infections. Common bacteria that lead to gangrene include Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Clostridium species.
3. Trauma or Injury
Serious injuries, such as those caused by car accidents, deep cuts, or burns, can damage blood vessels and lead to gangrene. Surgery wounds that become infected can also trigger gangrene.
4. Chronic Diseases
People with chronic conditions like diabetes, peripheral artery disease, or Raynaud’s disease are at higher risk of developing gangrene. These conditions can impair blood flow or increase the risk of infection.
5. Immunosuppression
Those with weakened immune systems, such as individuals with HIV/AIDS or cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, are at a higher risk of developing infections that can lead to gangrene.
Also Read: What is the Most Effective Treatment for Gangrene?
Symptoms of Gangrene
The symptoms of gangrene vary depending on the type, but common signs include:
- Skin discoloration: Affected areas may turn black, blue, or red.
- Severe pain: Pain can be intense, particularly in gas gangrene.
- Swelling and blisters: Affected areas may swell or develop fluid-filled blisters.
- Foul-smelling discharge: Wet gangrene often produces a foul-smelling pus.
- Loss of sensation: As tissues die, numbness or loss of sensation may occur.
- Fever and malaise: Infections can cause fever and a general feeling of illness.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Gangrene
Gangrene is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging tests (such as X-rays or MRIs), and laboratory tests (like blood cultures to detect infections). Immediate medical intervention is crucial to prevent the spread of tissue death.
Treatment Options Include:
- Surgery: Removing the dead tissue (debridement) is often necessary to stop gangrene from spreading. In severe cases, amputation may be required.
- Antibiotics: In cases of bacterial infection, antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the infection.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: This treatment involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room, which helps promote healing by increasing oxygen levels in the blood.
- Vascular Surgery: To restore blood flow to the affected area, surgery may be performed on the blood vessels.
- Wound Care: Keeping the affected area clean and protected is essential for recovery.
Also Read: 10 Essential Tips for Managing Diabetic Foot: Prevention and Care for Healthy Feet
Prevention of Gangrene
Taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing gangrene, especially if you have underlying health conditions:
- Manage chronic conditions: Keeping diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic conditions under control can help maintain healthy blood circulation.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and significantly increases the risk of gangrene.
- Maintain good hygiene: Proper wound care and hygiene can prevent infections from taking hold.
- Regular check-ups: If you have circulatory issues or diabetes, regular medical check-ups can help detect problems early.
Risk Factors for Gangrene
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing gangrene, including:
- Diabetes: Diabetes damages blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of gangrene, particularly in the feet and toes.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD): Poor circulation due to narrowed arteries can lead to gangrene.
- Smoking: Smoking restricts blood flow and contributes to vascular diseases that can cause gangrene.
- Frostbite: Extreme cold can damage tissues and reduce blood flow, potentially leading to gangrene.
Conclusion
Gangrene is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical attention. Understanding its causes, types, and symptoms is vital for early detection and treatment. By managing risk factors such as poor circulation, infections, and chronic health conditions, you can reduce the likelihood of developing gangrene. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms of gangrene, seek immediate medical care to prevent severe complications.




