Breast health is a vital aspect of overall well-being, and understanding the nature of it is crucial for both prevention and treatment. This guide delves into the various symptoms and treatments associated with it, offering a thorough understanding to help women navigate this complex issue.
Introduction
Breast lumps can be a source of anxiety and confusion for many women. While the discovery of a lump in the breast can be alarming, it is essential to remember that not all breast lumps are cancerous. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify breast lumps by exploring their symptoms, causes, and the range of treatments available. We will also discuss preventive measures and the importance of regular breast examinations.
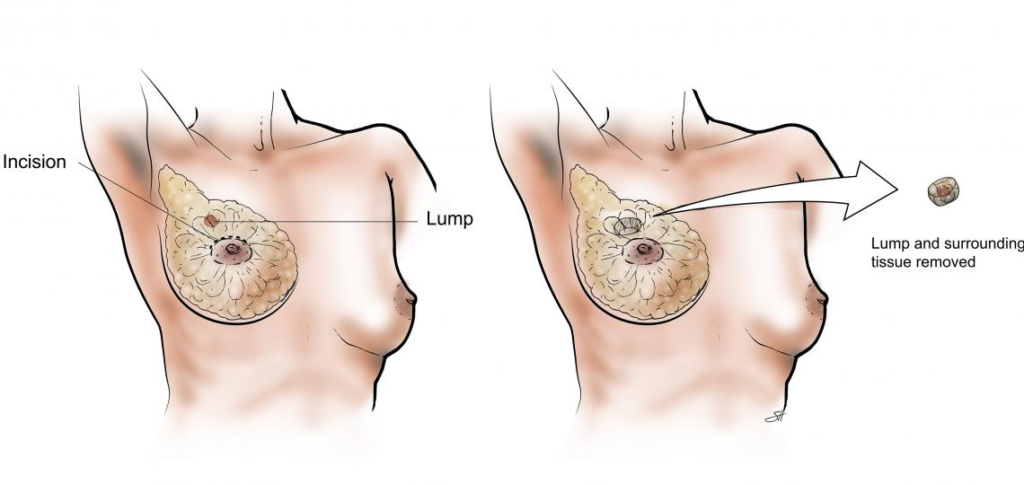
Understanding Breast Lumps
What Are Breast Lumps?
Breast lumps are masses that can form in the breast tissue. They can vary significantly in size, shape, and texture. Some lumps are benign (non-cancerous), while others can be malignant (cancerous). Understanding the differences and knowing what to look for can help in early detection and treatment.
Types of Breast Lumps
There are several types of breast lumps, each with distinct characteristics:
- Fibroadenomas: These are benign tumors that are most common in young women. They are usually round, firm, and movable.
- Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast tissue, often changing size with the menstrual cycle.
- Fibrocystic Changes: A combination of fibrous tissue and cysts that can cause lumpy, tender breasts, especially before menstruation.
- Lipomas: Soft, fatty lumps that are generally harmless.
- Malignant Tumors: Cancerous lumps that can be hard, irregularly shaped, and attached to the surrounding tissue.
Symptoms of Breast Lumps
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of breast lumps can vary, but some common signs to watch for include:
- A palpable mass in the breast or underarm area.
- Changes in the size, shape, or appearance of the breast.
- Skin changes, such as dimpling, redness, or puckering.
- Nipple discharge, which may be clear, bloody, or another color.
- Pain or tenderness in the breast.
When to See a Doctor?
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any of the following:
- A new lump that feels different from the rest of your breast tissue.
- A lump that does not go away after your menstrual cycle.
- Any significant changes in breast size, shape, or skin texture.
- Persistent pain in one area of the breast.
Diagnosis of Breast Lumps
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing a breast lump is a physical examination by a healthcare provider. They will assess the size, shape, and texture of the lump and check for any other signs of abnormalities.
Imaging Tests
Several imaging tests can help diagnose breast lumps:
- Mammography: An X-ray of the breast that can reveal abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the breast tissue, helping to distinguish between solid and fluid-filled lumps.
- MRI: Provides detailed images of the breast tissue and is often used in conjunction with other tests.
Biopsy
If imaging tests suggest an abnormality, a biopsy may be necessary. This involves taking a small sample of the lump tissue for further analysis to determine if it is benign or malignant.
Causes of Breast Lumps
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, especially related to the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause, can cause breast lumps. These lumps often disappear on their own and are generally benign.
Breast Injuries
Injuries to the breast can lead to the formation of lumps. These are usually caused by trauma and can result in scar tissue or fat necrosis, where the fatty tissue in the breast is damaged.
Infections
Breast infections, such as mastitis, can cause lumps. These infections are more common in breastfeeding women and can result in painful, swollen lumps that may be accompanied by fever and redness.
Genetic Factors
A family history of breast lumps or breast cancer can increase the risk of developing breast lumps. Genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are known to elevate the risk of breast cancer.
Treatments for Breast Lumps
Monitoring and Follow-Up
For benign breast lumps, doctors may recommend regular monitoring to ensure they do not grow or change. This may involve periodic physical exams and imaging tests.
Medications
Certain medications can help manage symptoms associated with breast lumps:
- Hormonal Therapy: Used to treat lumps related to hormonal changes.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed for lumps caused by infections.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort.
Surgical Options
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a breast lump:
- Lumpectomy: Removal of the lump and a small margin of surrounding tissue.
- Mastectomy: Complete removal of the breast, typically used for large or multiple cancerous lumps.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It is often used after surgery to ensure all cancerous cells are eliminated.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be administered orally or intravenously and is often used in conjunction with other treatments.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Some women opt for alternative and complementary therapies to manage breast lumps. These can include:
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs are believed to help with hormonal balance and reduce lump size.
- Acupuncture: Can help alleviate pain and improve overall well-being.
- Lifestyle Changes: Diet, exercise, and stress management can play a role in breast health.
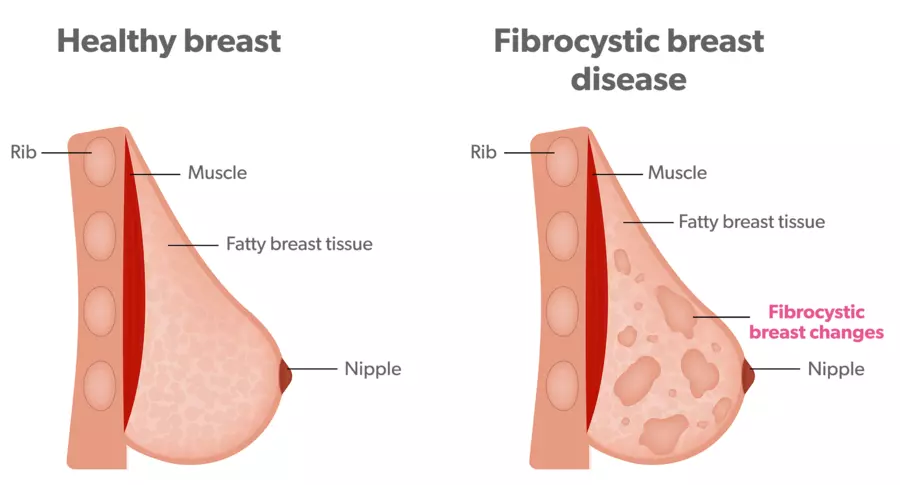
Preventing Breast Lumps
Regular Self-Examinations
Performing regular breast self-examinations can help detect changes early. It is recommended to do this monthly, ideally a few days after your menstrual period ends.
Routine Screenings
Mammograms and other routine screenings are crucial for early detection of breast abnormalities. Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for screening frequency based on your age and risk factors.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing it. This includes:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Staying physically active to maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Smoking: Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding smoking can lower the risk of breast cancer.
Breast Lumps and Menstrual Cycle
Hormonal Influence
Hormones play a significant role in the development of it, particularly estrogen and progesterone. These hormones fluctuate throughout the menstrual cycle, affecting breast tissue.
Cyclical Changes
Many women experience cyclical changes in their breasts, which can include the formation of lumps. These lumps are typically benign and related to the menstrual cycle. They often become more noticeable just before menstruation and may disappear afterward.
Managing Symptoms
To manage symptoms related to cyclical breast lumps, consider the following:
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: NSAIDs like ibuprofen can help alleviate discomfort.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warmth to the breasts can reduce pain and swelling.
- Supportive Bras: Wearing a well-fitted, supportive bra can minimize discomfort.
Breast Lumps During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy and breastfeeding cause significant hormonal changes, which can lead to the development of it. These are usually benign and related to milk production and changes in breast tissue.
Common Types of Lumps
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the following types of lumps are common:
- Galactoceles: Milk-filled cysts that develop when a milk duct becomes blocked.
- Mastitis: An infection of the breast tissue that can cause painful lumps, often accompanied by redness and fever.
Treatment and Management
For benign lumps related to pregnancy and breastfeeding, treatment may involve:
- Frequent Feeding or Pumping: Helps prevent milk duct blockages.
- Antibiotics: For infections like mastitis.
- Warm Compresses and Massage: To relieve pain and encourage milk flow.
Breast Lumps in Men
Prevalence
While breast lumps are more common in women, men can also develop them. Male breast cancer, though rare, does occur and can present as a lump in the breast tissue.
Symptoms
Symptoms of it in men are similar to those in women and can include:
- A painless lump in the breast tissue.
- Changes in breast size or shape.
- Nipple discharge or retraction.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis involves physical exams, imaging tests, and biopsies. Treatment options for men are similar to those for women and may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Psychological Impact of Breast Lumps
Anxiety and Stress
Finding a breast lump can cause significant anxiety and stress. It is natural to fear the worst, but it is essential to remain calm and seek medical advice promptly.
Support Systems
Having a strong support system can help alleviate the emotional burden. This can include family, friends, and support groups for individuals facing similar challenges.
Professional Help
Mental health professionals can provide counseling and support to help manage the emotional impact of it. Therapy can offer coping strategies and emotional resilience.
FAQs
What are the common causes of breast lumps?
Common causes include hormonal changes, infections, injuries, and genetic factors. Understanding these can help in identifying and managing it effectively.
How can I tell if a breast lump is cancerous?
Only a medical professional can determine if a lump is cancerous through diagnostic tests like mammograms, ultrasounds, and biopsies. It is crucial to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
Are all breast lumps painful?
No, not all breast lumps are painful. Pain is not a reliable indicator of whether a lump is benign or malignant. Some cancerous lumps may be painless, while benign lumps can cause discomfort.
Can men develop breast lumps?
Yes, men can develop breast lumps, including male breast cancer. While rare, it is important for men to seek medical evaluation if they notice any changes in their breast tissue.
What is the best way to prevent breast lumps?
While not all breast lumps can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, performing regular self-examinations, and undergoing routine screenings can help detect and manage it early.
What should I do if I find a breast lump?
If you find a breast lump, it is essential to remain calm and schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and appropriate testing.
Conclusion
Understanding breast lumps, their symptoms, and treatments is essential for maintaining breast health. While the discovery of a lump can be alarming, it is important to remember that many breast lumps are benign and treatable. Regular self-examinations, routine screenings, and a healthy lifestyle are key components in the early detection and management of it. By staying informed and proactive, women can take control of their breast health and address any concerns promptly and effectively.

Our Doctors
Dedicated IR Center for Vascular Problems in Madhya Pradesh
DR. SHAILESH GUPTA
MD, PDCC (INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY) Consultant & Co-Director CVIC (Center Of Vascular & Interventional Care)
DR. ALOK KUMAR UDIYA
MD Radiology, PDCC (Neurointervention Radiology), PDCC ( HPB Intervention Radiology) FINR (Switzerland) & EBIR
Endovascular Surgeon & Consultant Interventional Neuroradiologist at Care CHL Hospital, Indore Co-director CVIC( center for vascular and interventional care)
DR. NISHANT BHARGAVA
Consultant Intervention Radiologist
MD Radiology, PDCC ( Neurointervention Radiology), FINR ( Fellowship in Neurointervention Radiology)
Co-director CVIC(Center for Vascular and Interventional Care)
Contact Details
Phone no.
0731 4675670
+91 9827760073
Facebook
https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100092538633553&mibextid=ZbWKwL
Instagram
https://instagram.com/cvic_center?igshid=ZGUzMzM3NWJiOQ==
Google My business
https://g.co/kgs/DrdV3T
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCP5TH5e4iQZkpDUgnLsgZhw
Pinterest
https://pin.it/5DzpX5Z
Twitter
https://x.com/cviccenter?t=01TclSrLFdu0K2re0Gs96w&s=08
LINKEDIN
https://www.linkedin.com/company/center-of-vascular-interventional-care/
Location –
Read More –
What is the Survival Rate for TACE Liver Cancer? – https://cvicvascular.com/what-is-the-survival-rate-for-tace-liver-cancer/
The Comprehensive Guide to Radiofrequency Ablation for Liver Cancer – https://cvicvascular.com/the-comprehensive-guide-to-radiofrequency-ablation-for-liver-cancer/
BRTO for Pediatric Patients: Special Considerations and Outcomes – https://cvicvascular.com/brto-for-pediatric-patients-special-considerations-and-outcomes/




