How Much Does AVM Embolization Cost?
Understanding AVM Embolization
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) embolization is a minimally invasive procedure aimed at treating abnormal connections between arteries and veins in the brain or spinal cord. The cost of this procedure can vary widely based on several factors, including the complexity of the AVM, the geographic location of the treatment center, and the specific requirements of the patient. This article delves into the various elements that influence the cost of AVM embolization, providing a comprehensive overview to help patients and their families make informed decisions.
Outline
| Heading | Sub-headings |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Understanding AVM Embolization |
| AVM Embolization Cost | Factors Influencing Cost |
| Overview of AVM | What is an AVM? |
| Signs and Symptoms | Recognizing the Signs |
| Importance of Treatment | Why Treat AVMs? |
| Cost Breakdown | Hospital Fees |
| Surgeon Fees | |
| Anesthesia Fees | |
| Pre-Operative Tests | |
| Post-Operative Care | |
| Geographical Variations in Cost | Costs in the United States |
| Costs in Europe | |
| Costs in Asia | |
| Insurance Coverage | Understanding Your Policy |
| Out-of-Pocket Expenses | |
| Navigating Insurance Claims | |
| Comparing Costs with Other Treatments | Surgical Removal |
| Radiosurgery | |
| Conservative Management | |
| Cost vs. Outcome | Efficacy of Embolization |
| Patient Recovery Rates | |
| Financing Options | Medical Loans |
| Payment Plans | |
| Financial Assistance Programs | |
| Potential Hidden Costs | Long-Term Medications |
| Follow-Up Visits | |
| Rehabilitation | |
| FAQs | What is the average cost of AVM embolization? |
| Does insurance cover AVM embolization? | |
| Are there financial assistance programs for AVM embolization? | |
| What factors influence the cost of AVM embolization? | |
| How do I compare costs across different hospitals? | |
| What are the long-term costs associated with AVM embolization? | |
| Conclusion | Making Informed Decisions |
AVM Embolization Cost
Factors Influencing Cost
The cost of AVM embolization can be influenced by numerous factors. These include the size and location of the AVM, the expertise of the medical team, the type of hospital or clinic, and the patient’s overall health. Additionally, costs can be affected by whether the procedure is performed as an emergency or a planned intervention. Understanding these factors is crucial for patients seeking to estimate the financial implications of their treatment.
Overview of AVM
What is an AVM?
An AVM is a tangle of abnormal blood vessels connecting arteries and veins, which can disrupt normal blood flow and oxygen circulation. Most AVMs occur in the brain or spine but can develop anywhere in the body. Symptoms can vary widely depending on the location of the AVM and may include headaches, seizures, or neurological deficits. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent serious complications, such as hemorrhagic strokes.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of AVMs is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, potentially reducing the risk of serious complications. The symptoms of AVMs can vary widely depending on their size and location, particularly if they are in the brain or spinal cord. Here are some common signs and symptoms to be aware of:
Headaches: One of the most common symptoms of a brain AVM is a headache. These headaches can be severe and persistent, often localized to the area of the AVM. In some cases, they may resemble migraines and can be accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
Seizures: Seizures are another frequent symptom of brain AVMs. These can range from mild to severe and may include convulsions, loss of consciousness, or temporary confusion. Seizures occur because the abnormal blood vessels can irritate the surrounding brain tissue, leading to abnormal electrical activity.
Neurological Deficits: Depending on the location of the AVM, patients may experience various neurological deficits.
Cognitive Changes: Cognitive changes are another potential symptom of brain AVMs. These can include problems with memory, concentration, and other cognitive functions. Patients may find it difficult to focus on tasks, remember important information, or make decisions.
Speech and Language Issues: AVMs located near the brain’s language centers can cause speech and language issues.
Hearing Problems: Hearing problems can occur if the AVM is located near the auditory pathways in the brain. Patients may experience hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), or difficulties understanding speech.
Visual Disturbances: AVMs in the brain can also cause visual disturbances. These may include blurred vision, double vision, or partial vision loss. Some patients may experience visual field cuts, where they lose vision in certain areas of their visual field.
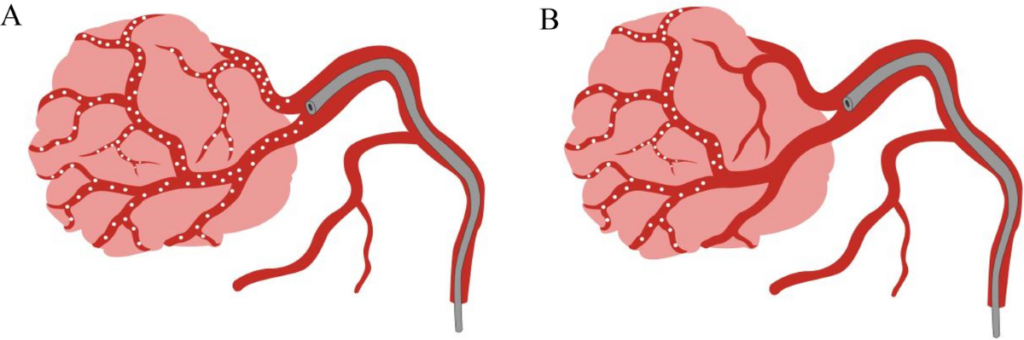
Behavioral Changes
Spinal AVM Symptoms
Sudden Onset of Symptoms
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of AVMs are crucial for preventing serious complications such as hemorrhagic stroke or permanent neurological damage. If you or a loved one experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Diagnostic imaging tests such as MRI, CT scans, or angiography can help identify the presence and extent of an AVM, allowing for appropriate treatment planning.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of AVMs is essential for early intervention and effective management of this complex condition. Understanding the potential symptoms can lead to timely medical evaluation and treatment, improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of life-threatening complications. If you suspect an AVM, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough assessment and appropriate care plan.
Importance of Treatment
Why Treat AVMs?
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are serious vascular anomalies that can have significant health implications if left untreated. Treatment is crucial for managing symptoms, preventing life-threatening complications, and improving the quality of life for patients. The following sections outline the key reasons why treating AVMs is of paramount importance.
Preventing Hemorrhagic Stroke
One of the most critical reasons to treat an AVM is to prevent hemorrhagic stroke. AVMs can rupture, leading to bleeding in the brain or spinal cord. Such hemorrhages can cause sudden and severe neurological deficits, loss of consciousness, and even death. The risk of rupture varies depending on the size and location of the AVM, but the overall annual risk is estimated to be between 2-4%. Treatment significantly reduces the likelihood of rupture, thereby decreasing the risk of a catastrophic event.
Reducing Neurological Deficits
AVMs can exert pressure on surrounding brain tissue, leading to various neurological deficits. These may include muscle weakness, sensory disturbances, coordination problems, and speech or vision issues. By treating the AVM, it is possible to alleviate these symptoms, prevent further neurological damage, and in some cases, restore normal function. Treatment options such as embolization, surgical resection, or radiosurgery can effectively reduce or eliminate the AVM, thereby relieving pressure on the brain.
Improving Quality of Life
Untreated AVMs can severely impact a patient’s quality of life. Chronic headaches, seizures, and other neurological symptoms can interfere with daily activities, work, and social interactions. By addressing the AVM, patients often experience significant improvements in their symptoms and overall well-being. Effective treatment can lead to fewer headaches, reduced seizure frequency, and improved cognitive and physical function, allowing patients to lead more fulfilling lives.
Managing Seizures
Seizures are a common symptom of brain AVMs, resulting from abnormal electrical activity caused by the vascular malformation. These seizures can range from mild to severe and can significantly disrupt daily life. Treatment of the AVM can reduce the frequency and severity of seizures, improving patient safety and independence. In some cases, seizure activity may be completely resolved following successful treatment.
Preventing Progressive Neurological Decline
If left untreated, AVMs can lead to progressive neurological decline. This decline occurs as the AVM continues to disrupt normal blood flow and exert pressure on brain tissue. Over time, patients may experience worsening symptoms and increased disability. Early and effective treatment can halt or slow this progression, preserving neurological function and preventing long-term complications.
Reducing the Risk of Secondary Conditions
AVMs can lead to secondary health issues if not addressed. For example, chronic bleeding from an AVM can cause anemia, and repeated seizures can lead to cognitive impairment. Additionally, untreated AVMs may increase the risk of developing hydrocephalus (accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain) due to disrupted blood flow dynamics. Treating the AVM reduces the risk of these secondary conditions, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
Treating an AVM often involves detailed diagnostic imaging and evaluation. This comprehensive assessment can reveal other underlying health issues that may not have been previously identified. By undergoing treatment, patients benefit from a thorough medical evaluation that can address additional health concerns, ensuring a holistic approach to their care.
Psychological Benefits
Living with an untreated AVM can cause significant psychological stress and anxiety. The constant fear of a potential hemorrhage or worsening symptoms can affect mental health. Successfully treating the AVM can provide psychological relief, reducing anxiety and improving mental health. Patients often report a greater sense of security and peace of mind following treatment.
Optimizing Long-Term Health Outcomes
Proactive treatment of AVMs can optimize long-term health outcomes. Early intervention reduces the risk of complications and promotes better recovery. Patients who receive timely and effective treatment are more likely to experience positive long-term health outcomes, including reduced risk of re-bleeding, lower incidence of chronic neurological issues, and improved overall life expectancy.
Facilitating Future Medical Interventions
Successfully treating an AVM can facilitate future medical interventions that may be necessary for other health conditions. Untreated AVMs can complicate other medical procedures due to the risk of bleeding and other complications. By addressing the AVM, patients are in a better position to safely undergo other medical treatments or surgeries they may need in the future.
Cost Breakdown
Hospital Fees
Hospital fees can constitute a significant portion of the total cost of AVM embolization. These fees cover the use of the operating room, recovery room, and hospital stay. Depending on the complexity of the procedure and the length of the hospital stay, these costs can vary widely.
Surgeon Fees
Surgeon fees are another major component of the total cost. These fees depend on the surgeon’s experience, the complexity of the AVM, and the time required for the procedure. Highly experienced surgeons or those working in renowned medical centers may charge higher fees.
Anesthesia Fees
Anesthesia is essential for ensuring patient comfort and safety during the procedure. Fees can vary based on the type of anesthesia used and the duration of the procedure. These fees cover the anesthesiologist’s time, expertise, and the use of anesthesia equipment.
Pre-Operative Tests
Before the procedure, patients typically undergo a series of pre-operative tests to assess their health and plan the embolization. These tests may include blood tests, imaging studies like MRI or CT scans, and other diagnostic procedures. The cost of these tests can add up, depending on the number and type of tests required.
Post-Operative Care
After the procedure, patients require monitoring and follow-up care to ensure a successful recovery. Post-operative care costs include hospital stay, medications, follow-up visits, and any additional treatments or rehabilitation that may be necessary. These costs can vary depending on the patient’s recovery progress and any complications that may arise.
Geographical Variations in Cost
Costs in the United States
In the United States, the cost of AVM embolization can range from $50,000 to $100,000 or more, depending on the hospital and location. Major medical centers in urban areas tend to charge higher fees compared to smaller hospitals or clinics in rural areas.
Costs in Europe
In Europe, the cost of AVM embolization can be lower than in the United States, ranging from €20,000 to €50,000. However, costs can still vary significantly between countries and even within regions of the same country, influenced by the healthcare system, hospital facilities, and medical professionals’ expertise.
Costs in Asia
In Asia, the cost of AVM embolization can vary widely. In countries like India and Thailand, the cost can be significantly lower, ranging from $10,000 to $30,000, while in more developed countries like Japan or South Korea, the costs can be comparable to those in Europe or the United States.
Insurance Coverage
Understanding Your Policy
Understanding your insurance policy is crucial for determining what portion of the AVM embolization cost will be covered. Insurance policies can vary widely in terms of coverage, co-pays, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums. It is important to review your policy details and speak with your insurance provider to clarify coverage specifics.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Even with insurance, patients may face significant out-of-pocket expenses. These can include co-pays, deductibles, and costs for services not covered by insurance. Patients should be prepared for these potential costs and consider them when planning for their procedure.
Navigating Insurance Claims
Navigating insurance claims can be a complex process. Patients should ensure they have all necessary documentation, including medical records, doctor’s notes, and detailed billing statements, to support their claims. Working closely with the hospital’s billing department and your insurance provider can help streamline the process and ensure that claims are processed efficiently.
Comparing Costs with Other Treatments
Surgical Removal
Surgical removal of an AVM, known as resection, is another treatment option. The cost of surgery can be higher than embolization, ranging from $60,000 to $150,000, depending on the complexity and location of the AVM, as well as the hospital and surgeon’s fees.
Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery, such as Gamma Knife or CyberKnife, is a non-invasive treatment that uses focused radiation to target and shrink the AVM. The cost of radiosurgery can range from $30,000 to $70,000, depending on the treatment center and technology used.
Conservative Management
In some cases, conservative management, which involves monitoring the AVM without active intervention, may be recommended. While this approach has lower immediate costs, it carries the risk of potential complications requiring future treatment. The long-term costs of conservative management can vary based on the need for regular imaging and monitoring.
Cost vs. Outcome
Efficacy of Embolization
Embolization is an effective treatment for AVMs, particularly for those located in difficult-to-reach areas or those with a high risk of bleeding. The success rate of embolization varies depending on the size and location of the AVM, as well as the expertise of the medical team. Patients who undergo embolization often experience significant symptom relief and a reduced risk of future complications.
Patient Recovery Rates
Recovery rates after AVM embolization can vary. Some patients recover quickly with minimal complications, while others may require extended recovery time and additional treatments. The overall success and recovery rates are influenced by factors such as the patient’s age, overall health, and the complexity of the AVM.
Financing Options
Medical Loans
Medical loans are available to help patients finance the cost of AVM embolization. These loans can cover the full cost of the procedure and are repaid over time with interest. Patients should research different loan options and choose one with favorable terms and interest rates.
Payment Plans
Many hospitals and clinics offer payment plans that allow patients to spread the cost of the procedure over several months or years. These plans can make the financial burden more manageable and reduce the need for large upfront payments.
Financial Assistance Programs
Some hospitals and non-profit organizations offer financial assistance programs to help patients with the cost of AVM embolization. These programs may provide grants, discounted services, or other forms of financial aid to eligible patients. Patients should inquire about available programs and apply if they meet the criteria.
Potential Hidden Costs
Long-Term Medications
After AVM embolization, patients may require long-term medications to manage symptoms or prevent complications. The cost of these medications can add up over time and should be considered when planning for the procedure.
Follow-Up Visits
Regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor the patient’s recovery and ensure the success of the embolization. These visits can include imaging studies, consultations with specialists, and additional tests, all of which can incur costs.
Rehabilitation
Some patients may require rehabilitation to recover fully from the procedure. This can include physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy, depending on the location and impact of the AVM. Rehabilitation costs should be factored into the overall financial plan for treatment.
FAQs
What is the average cost of AVM embolization?
The average cost of AVM embolization can range from $50,000 to $100,000 in the United States, with lower costs in other regions such as Europe and Asia.
Does insurance cover AVM embolization?
Insurance coverage for AVM embolization varies by policy. It is important to review your insurance details and speak with your provider to understand what is covered and any out-of-pocket expenses.
Are there financial assistance programs for AVM embolization?
Yes, some hospitals and non-profit organizations offer financial assistance programs to help patients cover the cost of AVM embolization. Patients should inquire about these programs and apply if they are eligible.
What factors influence the cost of AVM embolization?
The cost of AVM embolization is influenced by factors such as the size and location of the AVM, the expertise of the medical team, the type of hospital, and the patient’s overall health. Geographic location and whether the procedure is an emergency can also affect costs.
How do I compare costs across different hospitals?
To compare costs across different hospitals, patients should obtain detailed estimates from each facility, including all potential fees such as hospital, surgeon, anesthesia, and post-operative care costs. It is also helpful to consider the hospital’s reputation and the experience of the medical team.
What are the long-term costs associated with AVM embolization?
Long-term costs associated with AVM embolization can include medications, follow-up visits, and rehabilitation. Patients should consider these potential costs when planning for the procedure and explore financing options if needed.
Conclusion
Understanding the costs associated with AVM embolization is crucial for patients and their families. By considering all the factors that influence cost, comparing different treatment options, and exploring financing and insurance coverage, patients can make informed decisions about their care. AVM embolization offers a promising treatment option for managing this complex condition, with the potential for significant improvements in health and quality of life.
Our Doctors
Dedicated IR Center for Vascular Problems in Madhya Pradesh
DR. SHAILESH GUPTA
MD, PDCC (INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY) Consultant & Co-Director CVIC (Center Of Vascular & Interventional Care)
DR. ALOK KUMAR UDIYA
MD Radiology, PDCC (Neurointervention Radiology), PDCC ( HPB Intervention Radiology) FINR (Switzerland) & EBIR
Endovascular Surgeon & Consultant Interventional Neuroradiologist at Care CHL Hospital, Indore Co-director CVIC( center for vascular and interventional care)
DR. NISHANT BHARGAVA
Consultant Intervention Radiologist
MD Radiology, PDCC ( Neurointervention Radiology), FINR ( Fellowship in Neurointervention Radiology)
Co-director CVIC(Center for Vascular and Interventional Care)
Contact Details
Phone no.
0731 4675670
+91 9827760073
Facebook
https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100092538633553&mibextid=ZbWKwL
Instagram
https://instagram.com/cvic_center?igshid=ZGUzMzM3NWJiOQ==
Google My business
https://g.co/kgs/DrdV3T
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCP5TH5e4iQZkpDUgnLsgZhw
Pinterest
https://pin.it/5DzpX5Z
Twitter
https://x.com/cviccenter?t=01TclSrLFdu0K2re0Gs96w&s=08
LINKEDIN
https://www.linkedin.com/company/center-of-vascular-interventional-care/
Location –
Read More –
How long does it take for kidney to heal after PCNL? – https://cvicvascular.com/how-long-does-it-take-for-kidney-to-heal-after-pcnl/
What is the Success Rate of Tumor Embolization? – https://cvicvascular.com/what-is-the-success-rate-of-tumor-embolization/
What is a Renal Graft Biopsy? – https://cvicvascular.com/what-is-a-renal-graft-biopsy/