Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the legs. It can lead to serious complications if left untreated, such as pulmonary embolism, where the clot breaks free and travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow. Management of DVT and the role of venous stenting in its treatment is a multifaceted approach that involves immediate intervention, long-term management, and prevention of recurrence.
Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
DVT primarily affects the large veins in the lower leg and thigh, where the clot can block blood flow and cause swelling, pain, and redness. Factors that increase the risk of DVT include prolonged immobility, certain medical conditions, smoking, obesity, pregnancy, and a family history of blood clots.

Immediate Management of DVT
The immediate goals in managing DVT are to prevent the clot from growing and to reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism. Treatment options include:
- Anticoagulants: Also known as blood thinners, anticoagulants are the first line of treatment. They can’t dissolve the clot but can prevent it from enlarging and reduce the risk of more clots. Examples include warfarin, heparin, and newer oral anticoagulants like rivaroxaban.
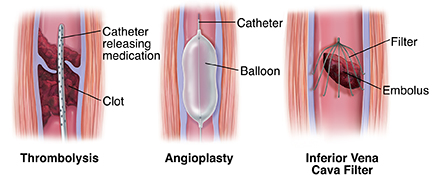
- Thrombolytics: In severe cases, especially where there is a significant threat to limb viability, thrombolytic therapy might be used to dissolve the clot. This is usually reserved for life-threatening situations due to the risk of bleeding.
- Compression Stockings: Wearing graduated compression stockings can help reduce the swelling associated with DVT.
Long-Term Management and Prevention
After the initial treatment, long-term management focuses on preventing the recurrence of DVT and managing post-thrombotic syndrome, a complication that can lead to pain, swelling, and ulcers in the affected limb. This includes:
- Continuing anticoagulation therapy as recommended by a healthcare provider.
- Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, weight management, and quitting smoking.
- Ongoing monitoring and follow-up care to adjust treatment as necessary.

The Role of Venous Stenting in DVT Management
Venous stenting is a treatment option for certain patients with DVT, particularly those with chronic venous insufficiency or post-thrombotic syndrome where there is long-term obstruction or damage to the veins.
What is Venous Stenting?
Venous stenting involves the placement of a metal mesh tube (stent) into the affected vein to keep it open and allow blood to flow more freely. It’s typically performed under imaging guidance.
Indications for Venous Stenting
Venous stenting is considered when:
- There is a significant venous outflow obstruction contributing to DVT or post-thrombotic syndrome.
- Conservative management has failed to alleviate symptoms.
- The patient has chronic venous insufficiency affecting quality of life.
The Procedure
The procedure is minimally invasive and usually performed on an outpatient basis. It involves:
- Inserting a catheter into the vein through a small incision.
- Using imaging techniques to guide the stent to the correct position.
- Expanding the stent to open up the vein and improve blood flow.
Post-Procedure Care
Following venous stenting, patients may need to continue anticoagulation therapy and wear compression stockings to support vein health and prevent clot formation around the stent.
Conclusion
Management of DVT requires a comprehensive approach that includes immediate treatment to prevent clot growth, long-term management to prevent recurrence, and interventions like venous stenting for specific cases. Advancements in medical treatments and interventions have significantly improved the outcomes for patients with DVT. However, early detection and treatment remain crucial for the best results. Consultation with a healthcare provider is essential for anyone who suspects they may have DVT or is at risk for the condition.
Our Doctors
Dedicated IR Center for Vascular Problems in Madhya Pradesh
DR. SHAILESH GUPTA
MD, PDCC (INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY) Consultant & Co-Director CVIC (Center Of Vascular & Interventional Care)
DR. ALOK KUMAR UDIYA
MD Radiology, PDCC (Neurointervention Radiology), PDCC ( HPB Intervention Radiology) FINR (Switzerland) & EBIR
Endovascular Surgeon & Consultant Interventional Neuroradiologist at Care CHL Hospital, Indore Co-director CVIC( center for vascular and interventional care)https://interventionradiologyindore.com/
DR. NISHANT BHARGAVA
Consultant Intervention Radiologist
MD Radiology, PDCC ( Neurointervention Radiology), FINR ( Fellowship in Neurointervention Radiology)
Co-director CVIC(Center for Vascular and Interventional Care)
Contact Details
Phone no.
0731 4675670
+91 9827760073
Facebook
https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100092538633553&mibextid=ZbWKwL
Instagram
https://instagram.com/cvic_center?igshid=ZGUzMzM3NWJiOQ==
Google My business
https://g.co/kgs/DrdV3T
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCP5TH5e4iQZkpDUgnLsgZhw
Pinterest
https://pin.it/5DzpX5Z
Twitter
https://x.com/cviccenter?t=01TclSrLFdu0K2re0Gs96w&s=08
LINKEDIN
https://www.linkedin.com/company/center-of-vascular-interventional-care/
Location
Read More –
Carotid Stenting in Neuro Intervention – https://cvicvascular.com/carotid-stenting-in-neuro-intervention/
Aneurysm coiling in Neuro Intervention – https://cvicvascular.com/aneurysm-coiling-in-neuro-intervention/
Pre-operative Embolisation of Tumor in Neuro Intervention – https://cvicvascular.com/pre-operative-embolisation-of-tumor/




