Aneurysms are potentially life-threatening conditions where a blood vessel bulges due to a weakness in the vessel wall. When untreated, they can rupture, causing serious complications. However, with advances in modern medicine, several treatments can prevent rupture and manage aneurysms effectively. Understanding the best treatment for an aneurysm can be crucial for both patients and their families, offering hope for a full recovery.
What Is an Aneurysm?
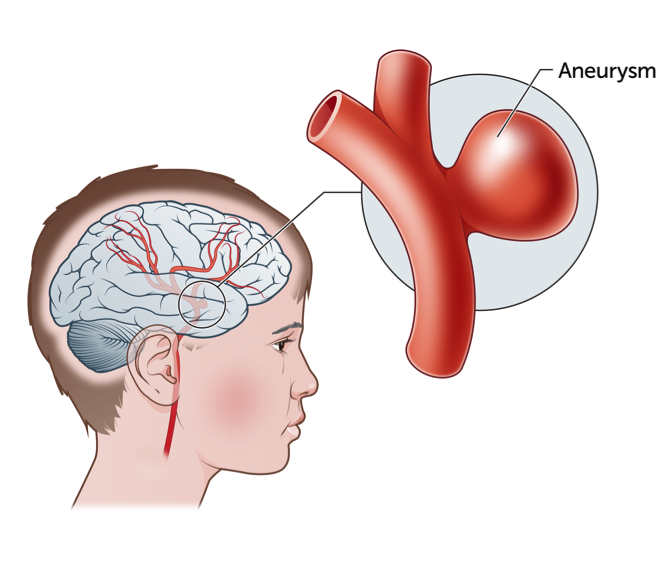
An aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel, typically caused by the weakening of the vessel wall. While aneurysms can develop anywhere in the body, they are most commonly found in the brain (cerebral aneurysm), aorta (aortic aneurysm), or arteries behind the knees. Most aneurysms are asymptomatic, but if they grow large or rupture, they can cause severe medical emergencies.
Types of Aneurysms
The three primary types of aneurysms are:
- Cerebral Aneurysms: Affect the blood vessels in the brain and may lead to strokes if they rupture.
- Aortic Aneurysms: Occur in the body’s largest artery, the aorta, which can cause massive internal bleeding.
- Peripheral Aneurysms: Found in the arteries other than the aorta, often in the legs or groin area.
Also Read: Conquer PAD in Legs: 10 Key Symptoms, Causes, and Best Treatment Options
Symptoms of an Aneurysm
Many aneurysms do not show noticeable symptoms until they are quite large or ruptured. However, some warning signs may include:
- Severe, sudden headaches (common in brain aneurysms)
- Back pain or abdominal pain (linked to aortic aneurysms)
- Numbness or weakness in limbs
- Shortness of breath or dizziness
Recognizing these symptoms early can be critical to getting the right treatment.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in determining the best treatment for an aneurysm. Medical professionals often use imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, and MRIs to detect aneurysms and assess their size and risk of rupture. Depending on the location and size of the aneurysm, doctors will tailor the treatment approach to minimize the chance of rupture and improve outcomes for the patient.
Also Read: Top 7 Best Treatment Options for Aneurysms: Effective Solutions for Better Health
Best Treatment for an Aneurysm
Now, let’s delve into the best treatment options for aneurysms, each tailored to the aneurysm’s type, location, and size.
1. Surgical Clipping
Surgical clipping is a common procedure used to treat brain aneurysms. In this procedure, a neurosurgeon places a small metal clip around the base of the aneurysm to cut off blood flow. This method prevents the aneurysm from rupturing by sealing it off entirely.
- When is it used? Primarily for cerebral aneurysms at high risk of rupture.
- Benefits: Proven to be highly effective with long-term success.
- Risks: As with any brain surgery, there’s a risk of infection, bleeding, or stroke.
2. Endovascular Coiling
Endovascular coiling is a minimally invasive procedure, ideal for aneurysms located in difficult-to-reach areas of the brain. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted through the groin and navigated to the aneurysm site. Once in place, small platinum coils are deployed inside the aneurysm, which promotes clotting and prevents rupture.
- When is it used? Often used for brain aneurysms when open surgery is too risky.
- Benefits: Less invasive than surgical clipping, with a shorter recovery time.
- Risks: There’s a small chance that the aneurysm could reopen over time, requiring additional treatment.
3. Open Aneurysm Repair
For aortic aneurysms, open aneurysm repair is a traditional surgical method. In this procedure, a surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen or chest, removes the damaged portion of the aorta, and replaces it with a synthetic graft.
- When is it used? Large or ruptured aortic aneurysms.
- Benefits: Effective for large aneurysms with a high risk of rupture.
- Risks: As an open surgery, it carries risks such as infection, blood loss, and longer recovery times.
Also Read: Understanding Aortic Aneurysm: Causes, Symptoms, and Life-Saving Treatment Options
4. Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR)
EVAR is a less invasive alternative to open aneurysm repair. A catheter is inserted through the groin to deliver a stent-graft to the aneurysm site. The stent-graft reinforces the weakened area of the blood vessel, reducing the risk of rupture.
- When is it used? Primarily for aortic aneurysms that haven’t ruptured yet.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive with faster recovery times.
- Risks: As with any procedure, there is a small risk of infection, bleeding, or graft failure.
5. Blood Pressure Management and Medication
For smaller aneurysms that are unlikely to rupture, doctors may recommend a non-surgical approach involving medication and close monitoring. Blood pressure-lowering medications, such as beta-blockers, help reduce stress on the weakened blood vessel walls.
- When is it used? Small, asymptomatic aneurysms.
- Benefits: Non-invasive approach, effective for managing small aneurysms.
- Risks: Without surgery, there’s always a slight risk that the aneurysm may grow over time.
Factors That Influence Treatment Choice
Choosing the best treatment for an aneurysm involves considering several factors, including:
- Size and location of the aneurysm
- Age and overall health of the patient
- Risk of rupture or other complications
- Patient preference after discussing the risks and benefits of each treatment option
Benefits of Regular Monitoring
For smaller aneurysms that do not require immediate surgery, doctors will often recommend regular imaging tests to monitor any growth. This approach allows for the aneurysm to be closely watched and treated if necessary, while avoiding unnecessary surgery.
FAQs
What is the safest treatment for an aneurysm?
Endovascular procedures like coiling or EVAR are often considered safer due to their minimally invasive nature, but the safest option depends on the aneurysm’s size and location.
How long does it take to recover from aneurysm surgery?
Recovery times vary. Endovascular procedures may have recovery times as short as two weeks, while open surgeries could require months of recovery.
Can medication treat an aneurysm?
Medication cannot cure an aneurysm, but it can help manage conditions that contribute to aneurysm growth, such as high blood pressure.
Is surgery always required for an aneurysm?
Not always. Small, asymptomatic aneurysms may only require monitoring and lifestyle changes to prevent growth.
What are the risks of not treating an aneurysm?
If left untreated, aneurysms may grow and eventually rupture, leading to life-threatening complications like internal bleeding or stroke.
Conclusion
The best treatment for an aneurysm depends on the aneurysm’s type, size, location, and the overall health of the patient. From surgical clipping and endovascular coiling for brain aneurysms to open aneurysm repair and EVAR for aortic aneurysms, medical advancements provide patients with more options than ever before. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing rupture and ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients. Always consult with a specialist to determine the most appropriate course of action for your condition.