Carotid Artery Disease: Preventing Stroke with Stenting and Angioplasty
When we think about strokes, we often imagine sudden and irreversible damage. But what if we told you that there are powerful, minimally invasive techniques that can prevent strokes before they even happen—especially if you’re at risk because of Carotid Artery Disease (CAD)?
In this comprehensive blog, we’ll walk you through:
- What Carotid Artery Disease is
- How it leads to strokes
- Modern techniques like angioplasty and stenting
- Who needs these procedures
- How they are performed
- Risks, benefits, and recovery
- How to prevent Carotid Artery Disease in the first place
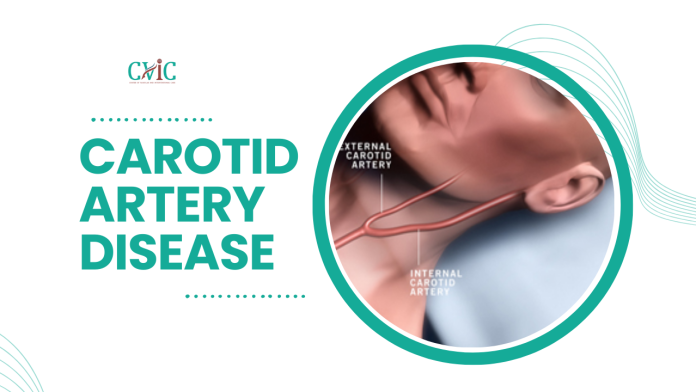
What Is Carotid Artery Disease?
Your carotid arteries are major blood vessels located on either side of your neck. They carry oxygen-rich blood from your heart to your brain. Over time, these arteries can become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of plaque (a mix of cholesterol, fat, and other substances). This condition is called Carotid Artery Disease.
The Problem with Plaque
As plaque builds up, it restricts the flow of blood to the brain. This can either:
- Completely block the artery, or
- Cause pieces of plaque to break off and travel to the brain
Both scenarios are leading causes of stroke.
How Common Is Carotid Artery Disease?
CAD affects millions globally, and many don’t even know they have it until it’s too late. According to studies, 15–20% of all strokes are linked to carotid artery blockages.
The good news? With early detection and modern intervention techniques, you can dramatically reduce your stroke risk.
Symptoms: Often Silent Until It’s Dangerous
Carotid Artery Disease is often called a “silent threat” because it may not cause noticeable symptoms until a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) occurs.
Signs of a TIA or stroke may include:
- Sudden numbness or weakness (especially on one side of the body)
- Trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Vision loss in one eye
- Sudden dizziness or loss of balance
These symptoms are medical emergencies—if you notice them, seek immediate help.
Diagnosis: How Do Doctors Detect It?
Diagnosis usually starts with:
- Physical exam: A doctor may hear a “bruit” (whooshing sound) in your neck
- Ultrasound (Doppler test): To visualize blood flow
- CT Angiography (CTA) or MRI: For detailed images of the arteries
- Cerebral Angiography (DSA): Gold standard for vascular evaluation
Treatment Options: Lifestyle, Medications, and Procedures
Mild Cases
- Lifestyle changes: Healthy diet, exercise, quitting smoking
- Medications: Blood thinners, statins, antihypertensives
Severe Cases
When the artery is significantly narrowed (usually >70%), your doctor might recommend angioplasty and stenting or carotid endarterectomy (surgical removal of plaque). This blog focuses on angioplasty and stenting—the minimally invasive route.
What Is Carotid Artery Angioplasty and Stenting?
Angioplasty is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked arteries. Stenting involves placing a tiny mesh tube inside the artery to keep it open.
This combination is a powerful stroke-prevention method—especially for patients who are not good candidates for open surgery.
Who Should Get Carotid Stenting?
You might be eligible if:
- Your carotid artery is narrowed >70% even without symptoms
- You’ve had a stroke or TIA and your artery is narrowed >50%
- You’re not a good candidate for surgery due to age or other health problems
The Procedure: Step-by-Step
- Preparation
- Performed in a hospital with an interventional radiologist or vascular surgeon
- You’ll be awake, but mildly sedated
- Accessing the Artery
- A small incision is made in the groin or arm
- A catheter is guided through blood vessels to the carotid artery using X-ray imaging
- Angioplasty
- A balloon is inflated to widen the artery
- Stenting
- A self-expanding stent is placed to keep the artery open permanently
- Completion
- Balloon is deflated and removed
- Blood flow is restored and monitored
The procedure usually takes 1–2 hours, and many patients go home within 24–48 hours.
Benefits of Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting
- Minimally invasive: No large incisions
- Quicker recovery: Especially compared to open surgery
- Effective stroke prevention: Especially in high-risk patients
- Less risk of nerve damage than traditional surgery
Risks and Complications
- Stroke (ironic, but rare during the procedure)
- Artery re-narrowing (restenosis)
- Bleeding at the catheter site
- Allergic reaction to contrast dye
These risks are rare and can be minimized with an experienced interventionalist and proper patient selection.
After the Procedure: What to Expect
- Mild soreness or bruising near catheter site
- Light activity for a few days
- Medications like blood thinners to prevent clots
Follow-up imaging is done periodically to check the stent and blood flow.
Life After Stenting: Stay Ahead of the Game
- Take your medications exactly as prescribed
- Control cholesterol, blood pressure, and diabetes
- Quit smoking
- Eat a heart-healthy diet (think Mediterranean)
- Regular exercise (under doctor guidance)
- Schedule follow-ups for imaging tests
Carotid Artery Disease vs. Coronary Artery Disease
| Feature | Carotid Artery Disease | Coronary Artery Disease |
|---|---|---|
| Affects | Arteries to the brain | Arteries to the heart |
| Risk | Stroke | Heart attack |
| Key Treatment | Stenting, endarterectomy | Angioplasty, bypass surgery |
Can You Prevent Carotid Artery Disease?
Yes—mostly! Here’s how:
- Eat less saturated fat and processed foods
- Keep blood pressure and cholesterol in check
- Get 30+ minutes of activity daily
- Don’t smoke
- Get regular check-ups, especially after age 50
If you have diabetes or a family history of stroke, be extra vigilant.
Myth-Busting: Common Misconceptions
- ❌ Only old people get Carotid Artery Disease
✅ Plaque starts building from a young age—though symptoms show later - ❌ Angioplasty is dangerous
✅ When performed by experts, it’s safe and effective - ❌ No symptoms = no problem
✅ CAD is often silent until a stroke happens. Screening matters.
Why Choose an Interventional Radiologist or Vascular Expert?
Interventional radiologists and vascular surgeons are highly trained specialists who:
- Use imaging to guide treatment
- Offer minimally invasive options
- Customize care plans for each patient
- Often perform angioplasty and stenting with precision and safety
Look for a center like CVIC in Indore or others with experienced hands.
FAQs: Quick Answers for the Curious
Q. How long does the stent last?
A: Most carotid stents are designed to be permanent, but regular follow-ups are needed.
Q. Is angioplasty painful?
A: It’s usually not painful—you may feel some pressure, but sedation keeps you comfortable.
Q. Can the blockage come back?
A: Rarely, but it can. That’s why lifestyle and follow-up care are critical.
Q. What’s the success rate?
A: Success rates range from 85–95% when done at high-volume centers.
Conclusion: Protect Your Brain, Live Smarter
Carotid Artery Disease is a major but preventable cause of stroke. Thanks to angioplasty and stenting, many patients now have a second chance—without open surgery, long hospital stays, or major complications.
If you or someone you love is at risk, don’t wait. Get screened, ask questions, and take control of your health.