Trans arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is an advanced medical procedure widely used in the field of interventional oncology, particularly for treating certain types of liver cancer. This blog post delves into the details of TACE, covering its mechanism, applications, benefits, risks, and what patients can expect during and after the procedure.
What is TACE?
Trans arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a minimally invasive procedure designed to target and destroy cancer cells in the liver. It combines two approaches: the local delivery of chemotherapy and the restriction of the tumor’s blood supply. The procedure is primarily used for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of primary liver cancer, especially in cases where the tumor is not suitable for surgical removal.
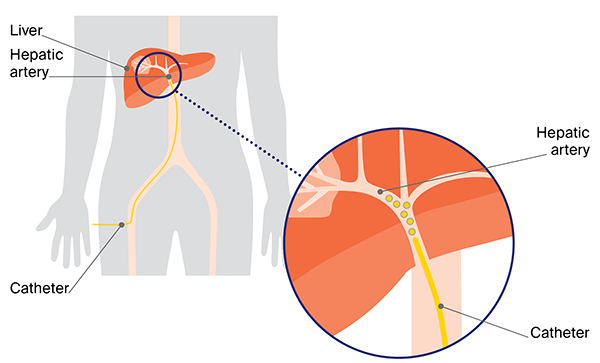
How Does TACE Work?
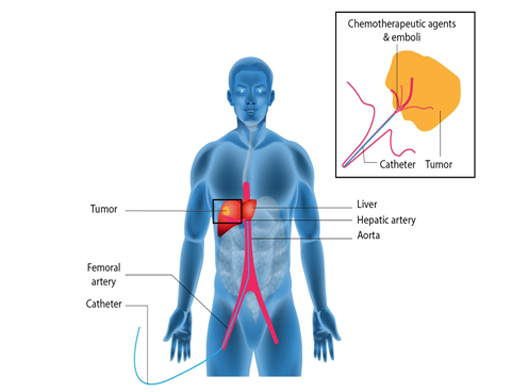
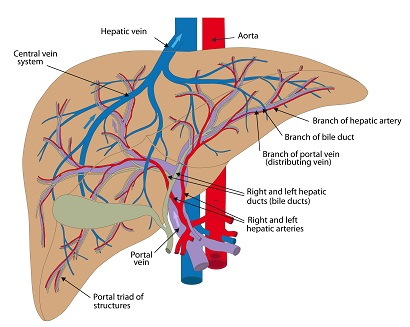
TACE exploits the fact that liver tumors typically receive their blood supply from the hepatic artery, whereas the rest of the liver tissue is primarily supplied by the portal vein. This selective delivery allows for a high concentration of chemotherapy agents to be administered directly to the tumor, minimizing systemic side effects. The process involves:
Catheter Insertion: Under local anesthesia and sedation, a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery in the groin and carefully guided through the blood vessels to the hepatic artery in the liver.
Chemotherapy Administration: Once in position, a high dose of chemotherapy drugs mixed with a contrast agent is infused directly into the artery feeding the tumor.
Embolization: Immediately following the chemotherapy infusion, tiny embolic agents are introduced through the catheter to block the artery, trapping the chemotherapy within the tumor and starving it of its blood supply.
Benefits of TACE
- Targeted Treatment: TACE delivers chemotherapy directly to the tumor, limiting the impact on healthy liver tissue.
- Reduced Side Effects: Compared to systemic chemotherapy, TACE typically results in fewer and less severe side effects.
- Procedure Efficacy: TACE has been shown to increase survival rates in patients with certain stages of liver cancer.
Risks and Considerations
While TACE is generally safe, it’s not without risks. Potential complications can include post-embolization syndrome (symptoms include fever, nausea, and abdominal pain), liver damage, infection, and blood clots. The procedure is not suitable for all patients, particularly those with severe liver dysfunction or abnormal blood flow between the liver and lungs.
The TACE Procedure
Prior to the procedure, patients undergo thorough evaluation including imaging tests to assess the liver’s anatomy and function. During TACE, patients may be awake but will receive medications to ensure comfort. Post-procedure, patients typically stay in the hospital for observation and to manage any immediate side effects. Recovery times can vary, with most patients resuming normal activities within a week.
Aftercare and Follow-Up
Follow-up care is crucial after TACE. Regular imaging tests (like MRI or CT scans) are performed to monitor the treatment’s effectiveness and to decide if additional sessions are necessary. Patients are also monitored for liver function and overall well-being.
Conclusion
TACE represents a vital tool in the fight against liver cancer, offering a blend of targeted chemotherapy and arterial embolization. While it provides a valuable option for patients with inoperable tumors, the decision to proceed with TACE should be made after a comprehensive discussion with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers, considering the individual patient’s condition, liver function, and overall health.
As research continues to evolve, the future may bring enhancements to TACE, including more effective chemotherapy drugs and embolic materials, potentially improving outcomes for patients with liver cancer.
Our Doctors
Dedicated IR Center for Vascular Problems in Madhya Pradesh
DR. SHAILESH GUPTA
MD, PDCC (INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY) Consultant & Co-Director CVIC (Center Of Vascular & Interventional Care)
DR. ALOK KUMAR UDIYA
MD Radiology, PDCC (Neurointervention Radiology), PDCC ( HPB Intervention Radiology) FINR (Switzerland) & EBIR
Endovascular Surgeon & Consultant Interventional Neuroradiologist at Care CHL Hospital, Indore Co-director CVIC( center for vascular and interventional care)
DR. NISHANT BHARGAVA
Consultant Intervention Radiologist
MD Radiology, PDCC ( Neurointervention Radiology), FINR ( Fellowship in Neurointervention Radiology)
Co-director CVIC(Center for Vascular and Interventional Care)
Contact Details
Phone no.
0731 4675670
+91 9827760073
Facebook
https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100092538633553&mibextid=ZbWKwL
Instagram
https://instagram.com/cvic_center?igshid=ZGUzMzM3NWJiOQ==
Google My business
https://g.co/kgs/DrdV3T
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCP5TH5e4iQZkpDUgnLsgZhw
Pinterest
https://pin.it/5DzpX5Z
Twitter
https://x.com/cviccenter?t=01TclSrLFdu0K2re0Gs96w&s=08
LINKEDIN
https://www.linkedin.com/company/center-of-vascular-interventional-care/
Location –
Read More –
Interventional Radiologists in Indore – https://cvicvascular.com/interventional-radiologists-in-indore/
Image-Guided Therapies in Indore – https://cvicvascular.com/image-guided-therapies-in-indore/
Vascular Imaging Services Indore – https://cvicvascular.com/vascular-imaging-services-indore/




